

How Lead Distribution Algorithms Impact Conversion Rates (Round-Robin vs AI Routing)
Content:
- What Is Lead Distribution and Why It Matters
- Overview of Lead Distribution Algorithms
- Round-Robin Lead Distribution: How It Works
- Pros and Cons of Round-Robin Routing
- AI-Based Lead Routing: How Intelligent Distribution Works
- Impact on Conversion Rates: Round-Robin vs AI Routing
- When to Use Each Algorithm
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Introduction
Lead distribution is a structural component of any revenue-generating system. While marketing teams focus on lead acquisition and sales teams concentrate on closing deals, the mechanism that connects these two functions—lead assignment—often remains underestimated. However, the way incoming leads are routed directly influences response time, qualification accuracy, and ultimately conversion rates.
As sales organizations scale, manual lead assignment becomes inefficient and error-prone. This has led to widespread adoption of automated lead distribution algorithms, with Round-Robin and AI-based routing emerging as the most common approaches. Understanding how these models work and how they affect performance metrics is critical for building a predictable and scalable sales operation.
What Is Lead Distribution and Why It Matters
Lead distribution is the process of assigning incoming prospects to sales representatives based on predefined logic or automated decision-making models. In modern CRM environments, this process operates continuously and at high velocity, especially in inbound-driven sales funnels.
The impact of lead distribution extends beyond operational convenience. Research consistently shows that faster lead response times significantly increase contact and qualification rates. If high-intent leads are delayed or assigned to underqualified representatives, the probability of conversion decreases regardless of lead quality. Effective CRM lead assignment ensures that opportunities are matched with the right resources at the right time.
Overview of Lead Distribution Algorithms
Lead distribution algorithms define the rules by which leads are routed within a sales system. These algorithms vary in complexity, from simple rotation logic to predictive, data-driven models. The choice of algorithm determines how well the system adapts to changes in lead volume, rep performance, and buyer behavior.
The most common categories include:
- Manual or semi-manual assignment
- Rule-based routing (e.g., by geography or company size)
- Round Robin lead distribution
- AI lead routing
While rule-based systems introduce structure, they remain static. In contrast, AI-driven approaches continuously adjust decisions based on historical outcomes and real-time signals.
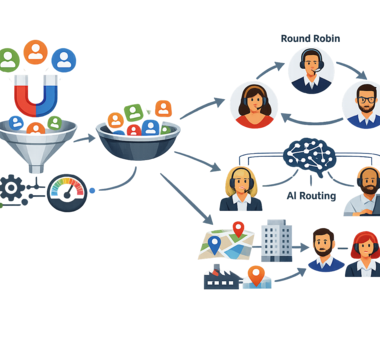
Round-Robin Lead Distribution: How It Works
Round-Robin lead distribution assigns leads sequentially across a predefined list of sales representatives. Each new lead is routed to the next available rep, creating an even distribution of workload. This method is widely used due to its simplicity and transparency.
From a system design perspective, Round-Robin does not evaluate lead attributes or sales rep specialization. The algorithm assumes that equal distribution results in fair opportunity allocation. This makes it easy to implement within most CRM platforms and reduces administrative overhead during early growth stages.
Pros and Cons of Round-Robin Routing
Round-Robin routing offers clear operational advantages, particularly for small or early-stage sales teams. Its primary strengths include:
- Predictable and equal lead allocation
- Minimal configuration and maintenance
- Perceived fairness among sales representatives
However, these benefits come with structural limitations that affect performance at scale:
- No consideration of lead intent or complexity
- No alignment with rep expertise or historical performance
- Reduced efficiency in heterogeneous sales teams
As deal sizes grow and buyer journeys become more complex, these constraints directly impact conversion rates and revenue efficiency.
AI-Based Lead Routing: How Intelligent Distribution Works
AI-based lead routing uses machine learning models to optimize lead-to-rep matching. Instead of rotating leads evenly, the system evaluates multiple variables, including lead behavior, demographic data, channel source, and past conversion outcomes.
Typical AI routing models analyze:
- Lead scoring signals (engagement, intent, fit)
- Sales rep win rates by segment
- Response speed and follow-up effectiveness
- Historical deal outcomes
By continuously learning from closed-won and closed-lost data, AI lead routing adapts in real time, improving assignment accuracy as the dataset grows.
Impact on Conversion Rates: Round-Robin vs AI Routing
The difference between Round-Robin and AI routing becomes measurable when evaluating downstream performance metrics. AI-based systems consistently outperform static distribution models in environments with sufficient data volume.
| Metric | Round-Robin | AI Routing |
| Response time optimization | Low | High |
| Lead–rep fit | Random | Predictive |
| Conversion rate uplift | Minimal | Significant |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
While lead routing vs round robin comparisons often focus on fairness, the critical variable is effectiveness. AI routing improves qualification accuracy and increases win probability, particularly for high-intent and high-value leads.
When to Use Each Algorithm
Choosing the right algorithm depends on organizational maturity, data availability, and sales complexity. There is no universal solution, but clear patterns emerge.
Round-Robin is suitable when:
- The sales team is small and homogeneous
- Deal complexity is low
- Limited historical data is available
AI routing is preferable when:
- Lead volume is high and variable
- Sales reps have specialized expertise
- The goal is to improve sales conversion rate through optimization
In many cases, companies transition from Round-Robin to AI routing as they scale and invest in sales automation AI.
Conclusion
Lead distribution algorithms are not neutral infrastructure components. They actively shape sales outcomes by influencing speed, relevance, and execution quality. While Round-Robin provides simplicity and fairness, it lacks the contextual intelligence required for modern, data-driven sales operations.
AI-based routing transforms lead distribution into a strategic lever. By aligning prospects with the most effective sales resources, organizations can systematically increase conversion rates, improve pipeline quality, and maximize revenue efficiency. For growth-oriented teams, intelligent routing is no longer optional—it is foundational.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Does AI lead routing really improve conversion rates?
Yes. AI routing increases conversion rates by matching leads with reps based on predictive performance rather than equal distribution. - Is Round-Robin still relevant for modern sales teams?
Round-Robin remains relevant for small teams or early-stage companies but becomes inefficient as complexity and scale increase. - How much data is needed for AI routing to be effective?
AI routing requires historical data on leads and sales outcomes. Effectiveness improves significantly once consistent patterns are established. - Can AI routing be integrated with existing CRM systems?
Most modern CRM platforms support AI-based lead routing either natively or through third-party integrations.

Lead Distribution Explained: How Smart Routing Increases ROI
Lead distribution is a foundational process in revenue operations that directly affects conversion rates, sales efficiency, and overall profitability. In competitive digital markets, generating leads is no longer enough - how those leads are assigned and processed determines whether marketing investments translate into revenue.





